In our domestic manufacturing blog series, we have embarked on a journey to uncover the transformative potential of domestic manufacturing initiatives in healthcare systems. In Part 1: Lessons Learned with COVID-19, we delved into the lessons learned from the global pandemic, shedding light on the significance of equitable access, addressing disparities, and building resilience.
In Part 2: Building Supply Chain Resilience, we also explored how countries strategically approached their health system readiness and resilience through domestic manufacturing, forging partnerships and securing funding for scaling up regional and local vaccine production. As we conclude this series, we now turn our attention to key recommendations that will pave the way for the success of domestic manufacturing endeavors.
Developing domestic manufacturing is capital intensive. Therefore, careful assessments of country needs and capacity along with holistic systems planning, must be made to mitigate risk and guarantee not only a successful business launch but also long-term sustainability.
Five guiding principles
To aid this process, IQVIA recommends the following set of guiding principles. These principles encompass considerations in identifying the appropriate therapeutic areas and types of products for domestic manufacturing, gaps and risk assessment of national capacity, all while aligning the country's perspective with a broader global impact.
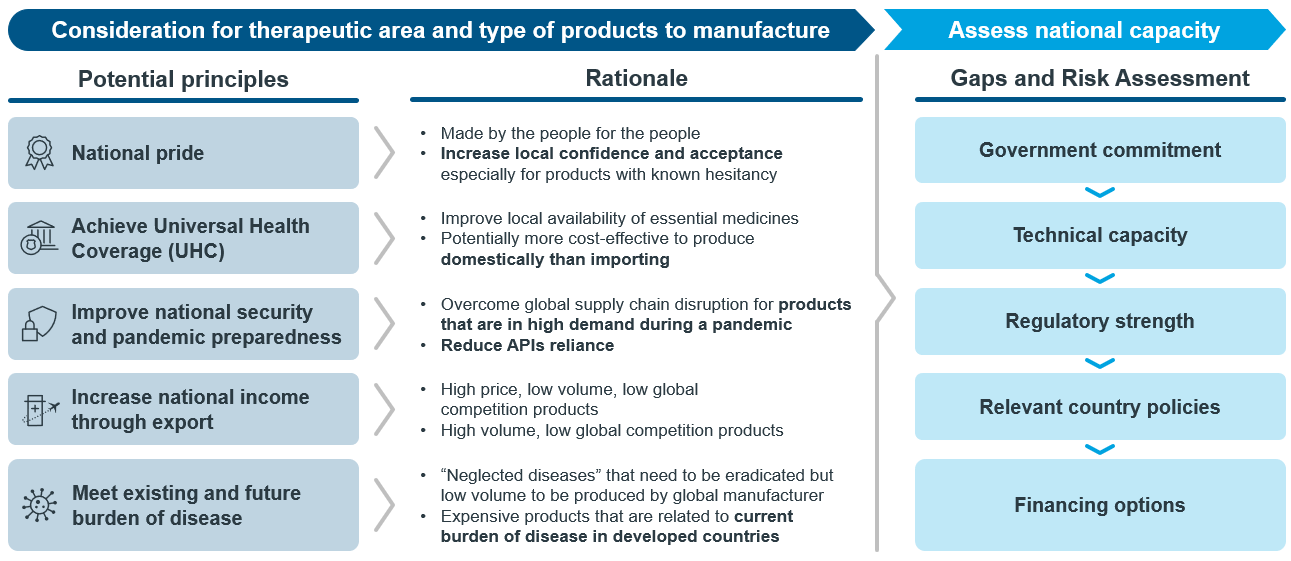
1. National Pride
Among many lessons learned from COVID-19, vaccine hesitancy is one of the major obstacles hampering effort to fight against the pandemic. Mistrust in vaccines developed in Western countries, for example, is one of the common factors behind vaccine hesitancy in African countries1. Therefore, having a locally made product may increase confidence and acceptance among the people.
2. Achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC)
Producing essential medicines domestically improves local availability and potentially be more cost-effective in the long run. Reducing reliance on imports and the vulnerability to supply chain disruptions, strengthens the UHC efforts in ensuring consistent access to life-saving treatments.
3. Improve national security and pandemic preparedness
Moving the production closer to end-users, especially for products that are expected to be in high demand during the pandemic, may resolve issues around global supply disruption. Considering to locally produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) will partially offset dependency on major API producers such as China and India and improve resilience of a health system in the event of another global pandemic.
4. Increase national income through export
Domestic manufacturing should also be geared to be globally competitive to ensure its commercial success. Global market competitive assessment should be made to identify opportunities and to consider selection of products to be manufactured.
5. Meet existing and future burden of disease
Identifying and addressing unmet needs of the local population, for example, neglected diseases which may have been eradicated in most parts of the world, results in expensive products.
Building positive impact
As governments from lower-income economies seek funding to develop domestic manufacturing from global donors, it is an opportunity to align national interests to fill in the global unmet needs and gaps whether in products, therapeutic areas, potential future diseases, pharmaceutical platforms and technologies.
Key global health players may play the central role in initiating innovative partnerships between the domestic manufacturers, the local governments, and the global industry, forging mutual understanding and favorable terms, coordinating a network and improving information sharing for future pandemic preparedness. We outline below how inputs from domestic manufacturing builds up towards positive impact at the national and global level.
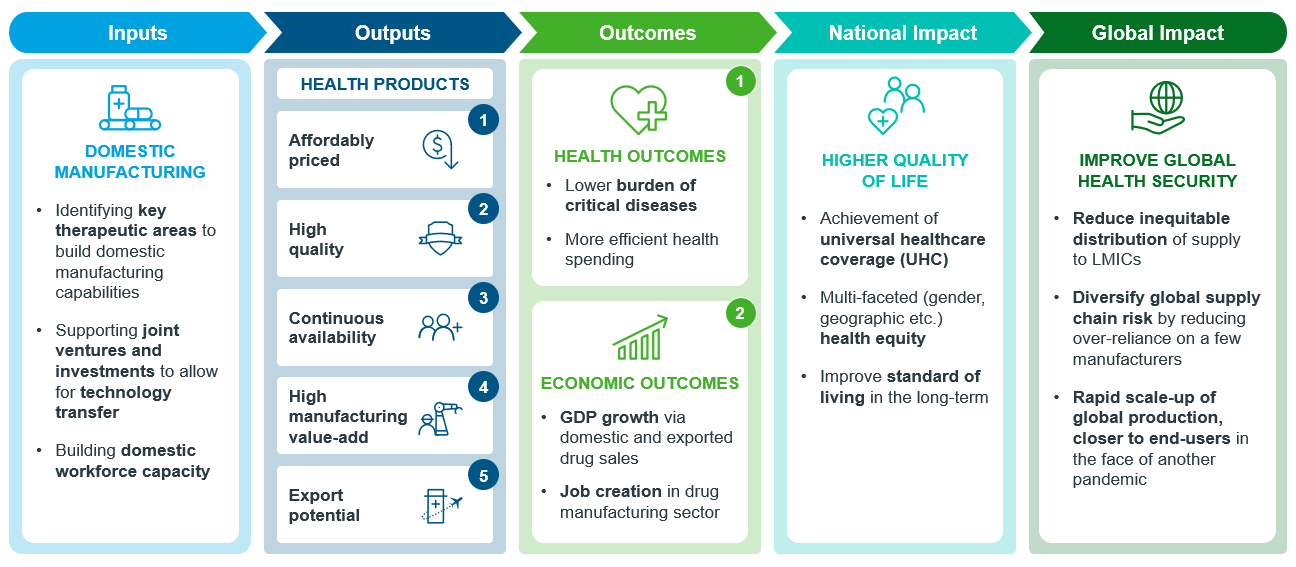
In conclusion, developing domestic manufacturing capabilities in healthcare systems holds tremendous promise for addressing critical challenges and fostering sustainable change. From bolstering national pride and achieving UHC to enhancing national security and increasing economic opportunities through exports, the benefits are multifold.
Moreover, by focusing on unmet local needs and forming innovative partnerships between domestic manufacturers, governments, and global industry players, there is potential to fill global gaps and improve health resilience against future global health threats.
By achieving the full potential of domestic manufacturing, we can make a lasting impact and ensure equitable access to essential life-saving treatments for all. For more information on improving population health outcomes, contact us.
References
1 https://blogs.worldbank.org/africacan/what-driving-covid-19-vaccine-hesitancy-sub-saharan-africa

IQVIA Public Health & Government
Working across the health system to address key barriers to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care while improving health outcomes using our data-driven and population-centric solutions.









